Photography is a collaboration of the technical with the creative. Once you've negotiated exposure, and how to manipulate light to paint your photos, it's time to think about composition, or how you construct your photos and place your subject or subjects within the frame to create an image.
Aspect ratio: what it is and why it matters
Did you go to see Wes Anderson's glorious fondant fancy of film The Grand Budapest Hotel? Did you notice how the size of the picture varied depended on the era being portrayed in the story? As the story moved between 1985, 1968, and 1932, the aspect ratio, or size of the image, jumped from 1.85:1 to 2.35:1 to 'Academy Ratio'. This was part of Anderson's story-telling technique: the aspect ratio provided viewers with a visual cue for each period of the narrative. It's also a reflection of the changes to aspect ratio that film and television have experienced over the years. But what about photographers? Where does aspect ratio come into stills?
Frame size
Maybe we need to back-track and establish precisely what we mean by 'aspect ratio' first. It's the size of the image expressed as a ratio, width to height. You'll often see film-making aspect ratios expressed as a value to 1 (like to 2.35:1 and 1.85:1 mentioned earlier), whereas the most common photography aspect ratios are 3:2, 4:3, and 1:1, although there are plenty more besides. If your image has an aspect ratio of 3:2, it will be three units wide and two high. When you come to print it, you might choose a 6×4" or a 12×8" print.
Originally, these aspect ratios were as a result of our film sizes. Lots of medium format cameras produced square, or 1:1, images; 35mm cameras used film that measured 36 by 24 millimetres, giving an aspect ratio of 3:2. What's referred to in the film-making world as 'Academy Ratio' is very close to 4:3. It's also the common aspect ratio you'll find in smartphone cameras as well as Micro Four Thirds and some medium format cameras. 16:9 is usual for recording video.
While our digital sensors might preserve these aspect ratios in their physical dimensions, at the press of a button I can switch between 3:2, 4:3, 16:9, and 1:1 on my camera. And when I import an image into Lightroom or edit it in Snapseed, I can select from 1:1, 3:2, 4:3, 5:4, 7:5, 8.5:11, 16:9, or settle upon an entirely idiosyncratic free-styled aspect ratio. But why would I want to?
Composing the frame
It's about composition, and dividing and filling your frame.
Photographers talk a lot about subject placement, about the different rules that can be used to divide the frame, and about negative space. All of these elements contribute to creating visually appealing, dynamic images that draw the eye. It follows, then, that the dimensions of the frame will have an impact on composition: on where you place your subject and how much space surrounds it and how you divide your frame.
Different rectangles
We've already written about the square crop here on Photocritic, and how the eye has a tendency to move around a square frame, as opposed to across it, which it does with a rectangular crop. When changing between 3:2 and 4:3 crops, are there any considerations that need to be made?
At its simplest, you have more space to fill with a 3:2 frame. Depending on your style and your subject, this can mean your subject has more room to breathe compared to a 4:3 crop. But it can also mean your subject has that bit too much space and feels a touch lost. You certainly need to be aware of this when you're shooting; and indeed if you intend to have prints made.
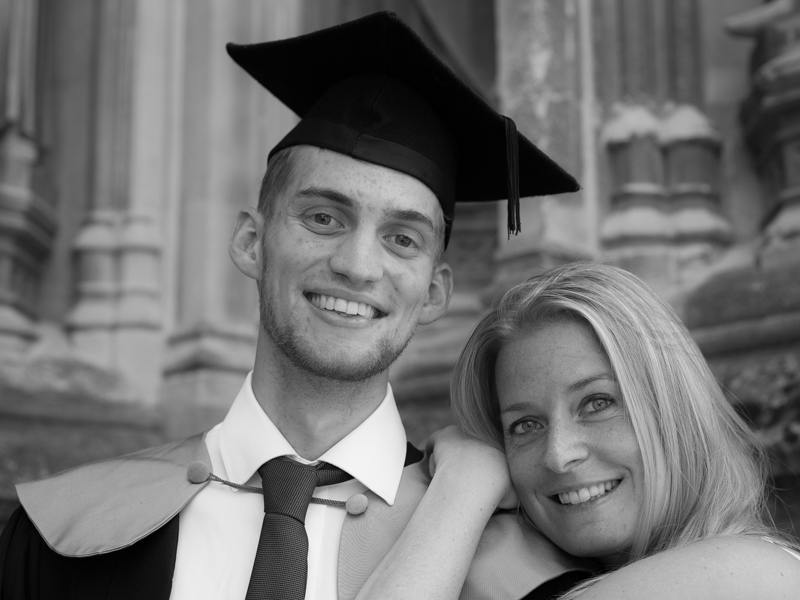
When I photographed my cousin on his graduation day, I adhered to my preferred 3:2 aspect ratio. It was how I approached filling the frame on the day and, consequently, how I processed the images afterwards. However, when my aunt had her prints made, she opted for a 24×18 canvas. I had to re-crop her favourite shot in a hurry. You can see both of them here. Can you see why I prefer the 3:2 aspect ratio in this instance? It doesn't feel nearly as squashed as the 4:3 version does.
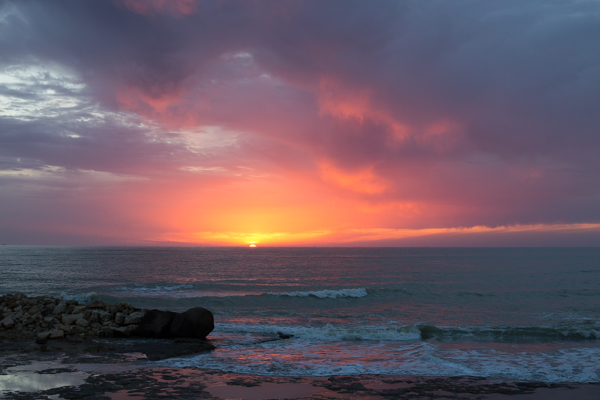
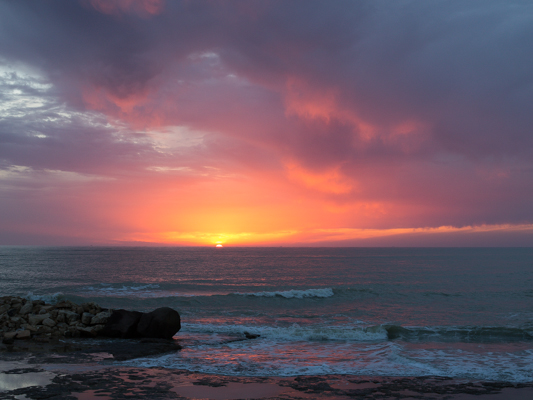
If you compare these sunset photos, you can see how much of the view the 4:3 version loses when compared with the 3:2 aspect ratio. It can prove difficult to fill the extra space in a landscape shot, but sometimes you need it, too.
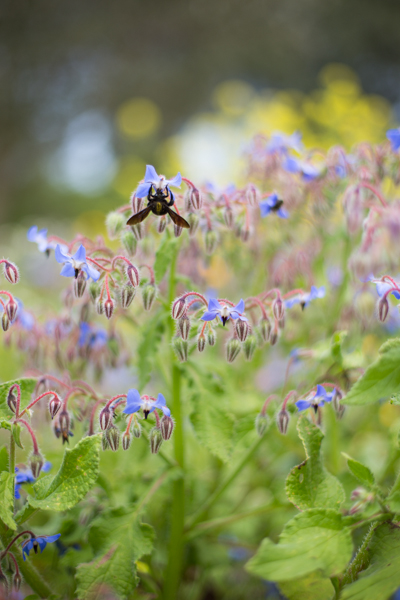
Of course, you don't have to adhere to 3:2 or 4:3 aspect ratios. I decided that 4:5 worked best for this bee enjoying the Sicilian springtime flowers. The more compact frame focused attention on the bee better than the larger 2:3 version.
Don't forget, if you switch from landscape to portrait orientation, then the aspect ratio will alter format accordingly. Width always goes first, thus 3:2 will change to 2:3 and 4:3 becomes 3:4. Or in the case of the bee, it's 4:5.
Opting for a different aspect ratio doesn't necessarily mean that you need to use a different compositional rule; however, in some circumstances, you might find the Golden Ratio preferable to the rule of thirds. It depends on your vision for the image. But do think about how much space you need around your subject. If you're struggling to fill it, think of trying 4:3; if it looks squashed, consider 3:2. Or try something else. Try not to feel too constrained by the constraints of aspect ratio.
But I will leave you with closing thoughts from xkcd. Who could put it better?
Trying the golden triangle
One of the first compositional rules that we learn is the rule of thirds. It's relatively simple but definitely effective: divide the frame into three, horizontally and vertically, and use the divisions to place your subject. But rules are made to be broken—once you understand them properly, that is—or at least adapted and challenged. If you're looking to leave behind the rule of thirds but still want place your faith in geometrically validated subject-placement, try the golden triangle.
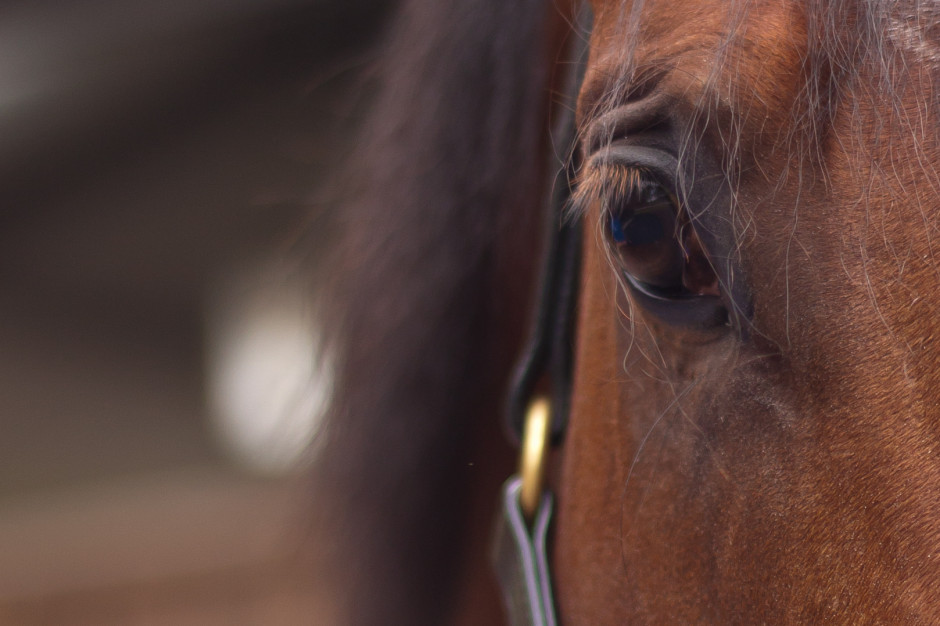

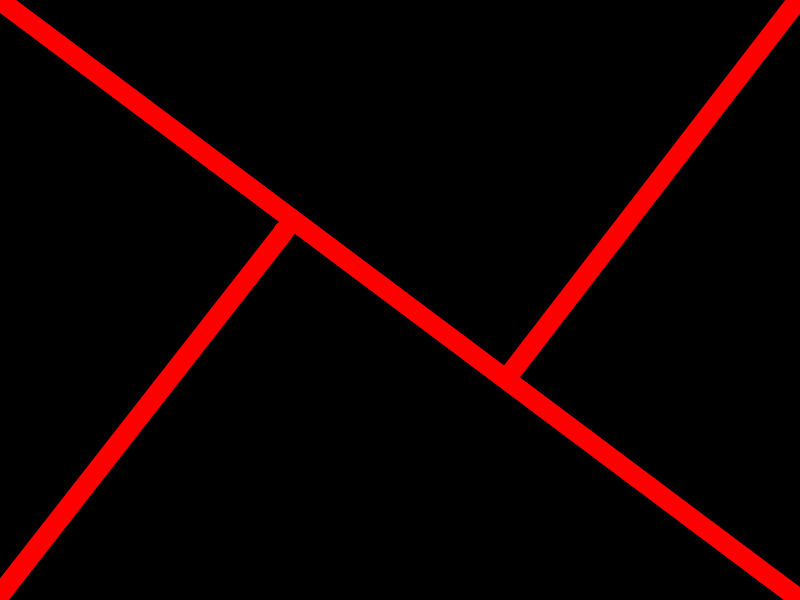
Determining the golden triangle
Draw an imaginary diagonal line across your frame. Now draw imaginary lines from the other two corners, which each meet the long line at right angles. It should look something like this:
Your points-of-interest are where the lines meet. Use them to place your focal point, for example the eyes in portraits, and use the lines to divide your frame and draw the eye to the focal point to help create dynamic images.
Why use the golden triangle?
On a mundane and practical level, it's easier for some people to visualise the triangle than it is the rule of thirds. Moving towards a more creative purpose, by using triangles to compose your frame you're introducing a strong compositional shape to it with a great sense of balance pitted against a precarious point. And triangles have a nifty way of retaining the attention of the eye within the frame: the eye moves from one point to another in a continuous loop.
[gallery ids="6953,6954,6955"]
Quite specifically with the golden triangle, you give yourself a means of dividing the frame in a way that is frequently more pleasing to the eye than a horizontal or vertical split. As well as using the lines to draw the eye to focal points, the use of triangles in the frame brings balance to the image. Think of one half as blue and the other as yellow. Or shadow versus light.
By counter-poising the two points-of-interest against each other, you can enhance the sense of balance in the frame. You get dynamism and balance in one go: brilliant.
Putting it into practice
It's all very well knowing the theory - what about the practice? Try portraits with your subject leaning into the frame and the eyes on a point-of-interest. Use the rule to place bridges in your frame, and have the eye travel along them to a focal point. Just give it a try - you never know!