Lensational's founders realised how photography could bring an emotional and financial strength to women across the world, whether through giving them the ability to express themselves or the chance to generate a small income.
The epic CES 2015 round-up
The great Photokina 2014 round-up
Keeping track of everything new that's announced at Photokina can feel like something of a labour of Sisyphus. So rather than cover every new product with an individual article and drive everyone to distraction, we've opted to summarise as many as we can in one place. This is Photokina 2014. Enjoy!
Canon
After what amounts to years of speculation, Canon has finally announced the EOS 7D mark II. The basic spec: APS-C, 20 megapixel sensor; ISO 100 to 16,000 but expandable to 51,200; dual DIGIC 6 processors; 65-point auto-focus; top shooting speed of 10 frames-per-second; and built-in GPS. All for $1,800, body-only.
Three new lenses have joined the line-up, too: an EF-S 24mm ƒ/2.8 STM for $149.00; an EF 24-105mm ƒ/4.0L IS STM for $599; and the EF 400mm ƒ/4.0L DO-IS II (USM) at $6,899.
There are also three new compact cameras. The premium G7X with its 1", 20 megapixel sensor and DIGIC 6 processor; top sensitivity of ISO 12,800; and a 24 to 100mm lens with a maximum aperture of ƒ/1.8 at its widest and ƒ/2.8 at the telephoto end, for $700. The SX60 superzoom with its 65× optical zoom for $550. And the N2, which, like the Powershot N, leaves me baffled.
Fujifilm
Fujifilm announced an update to its much-loved X100-series; the X100T. This one comes with an improved hybrid viewfinder, enhanced controls, and faster shuttre speeds. All for $1,300, in either black or silver.
The X20 has been upgraded to the X30. The improvements to Fuji's point-and-shoot focus on a new viewfinder and a tilting 3" high-res LCD. You can order one for £600.
There were also two new lenses: the X-F 56mm ƒ/1.2 R APD (85mm quivalent in 35mm format) for $1,500. (APD is apodisation. It is designed to give even smoother bokeh than the normal XF56. Great for portrait work.) And the weather resistant 50-140mm ƒ/2.8 R LM OIS WR at £1,600.
And don't forget the graphite-look X-T1 for $1,500 body-only.
Joby
Roll-up, roll-up, get your suction cups from Joby! Adding to its range of twisty, bendy, go-anywhere camera support devices, Joby has unveiled two suction cups, designed to provide industrial-strength hold on all types of smooth, clean, and non-porous surfaces. One has a locking arm, that's best for use in vibration-prone situations, such as in cars or on board boats (£33). The other has a Gorilla-pod arm, a quick-twist, flexible option that's better for windows, walls, and inside cars (£25).
[gallery columns="2" ids="6976,6975"]
There's also the Pro Sling Strap, designed for dSLRs, to keep your camera close to your body but easy to pull up to your eye (£57); the GorillaPod Focus + Ballhead X is the strongest and largest GorillaPod to date (£140); and the Flash Clamp and Locking Arm, which helps to transform everyday objects into lighting assistants with the two articulating ball joints that let you position your flash at any angle (£35).
[gallery ids="6979,6978,6977"]
Leica
Leica announced a laundry list of new cameras at Photokina:
- Leica M 60 Edition - an LCD-less camera, limited to 600 units, and costing $18,500 with a 35 Summilux stainless steel lens
- M-A
- X - Type 113; and X-E
- S - Type 007; and S-E
- V-Lux - Type 114
- D-Lux - Type 109, basically a Panasonic LX100
And a goodly selection of lenses, too. Leica enthusiasts couldn't have known which way to look first!
Nikon
Nikon's big announcement was the D750: an FX-format camera with 24 megapixel sensor and EXPEED 4 processor, 51-point autofocus system, sensitivity ranging from ISO 100 to 12,800, a tilting LCD, built-in wi-fi, all crammed into a smaller-than-expected body. For $2,300, body-only.
There was also the new Nikkor AF-S 20mm ƒ/1.8G ED and the SB-500 Speedlight.
Olympus
[gallery ids="6969,6968,6967"]
As well as announcing the E-PL7, Olympus brought out its E-M1 in silver (body-only for $1,400) and a new 40-150mm ƒ/2.8 lens for $1,500.
Panasonic
Panasonic came up with two new cameras and a new lens, together with the re-branded Leica cameras under the V-Lux and D-Lux badges.
[gallery ids="6966,6965,6964"]
The new LX100 camera is available for $900. It has a Micro Four Thirds sensor, a 4-75mm Leica DC lens (ƒ/1.7-2.8), and comes with an external flash. The GM5 mirror-less camera comes in black or red, with a 12-32mm lens, for $900.
And there's also the Panasonic G Vario 35-100mm ƒ/4.0-5.6 ASPH lens for G-series cameras, costing about $400.
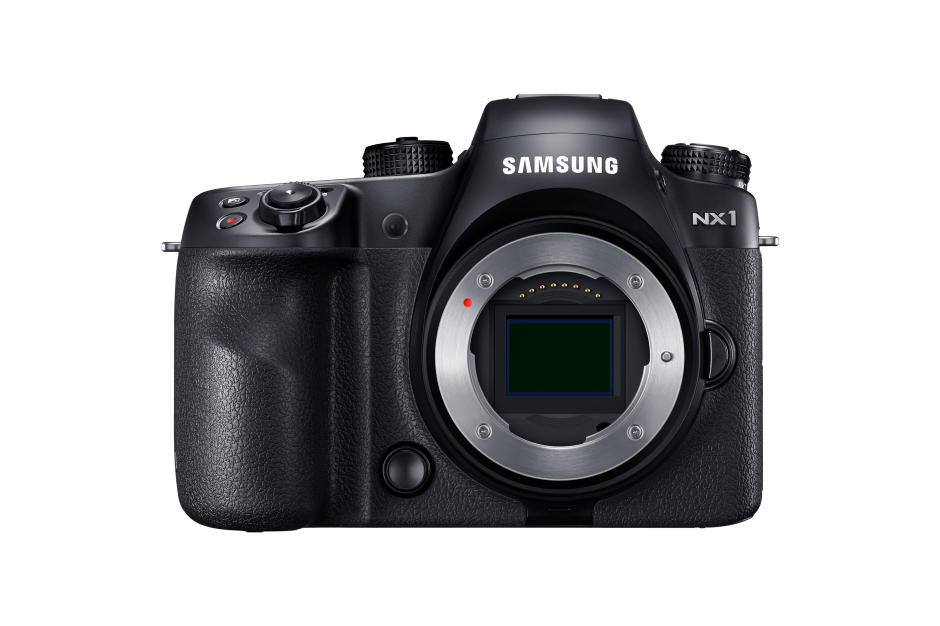
Samsung
Samsung let loose a new camera, lens, grip, battery, and charger on the public in Köln. The camera is the 4K-video-enabled 28 megapixel NX1 for $1,500 body-only and the lens the 50-150mm S.
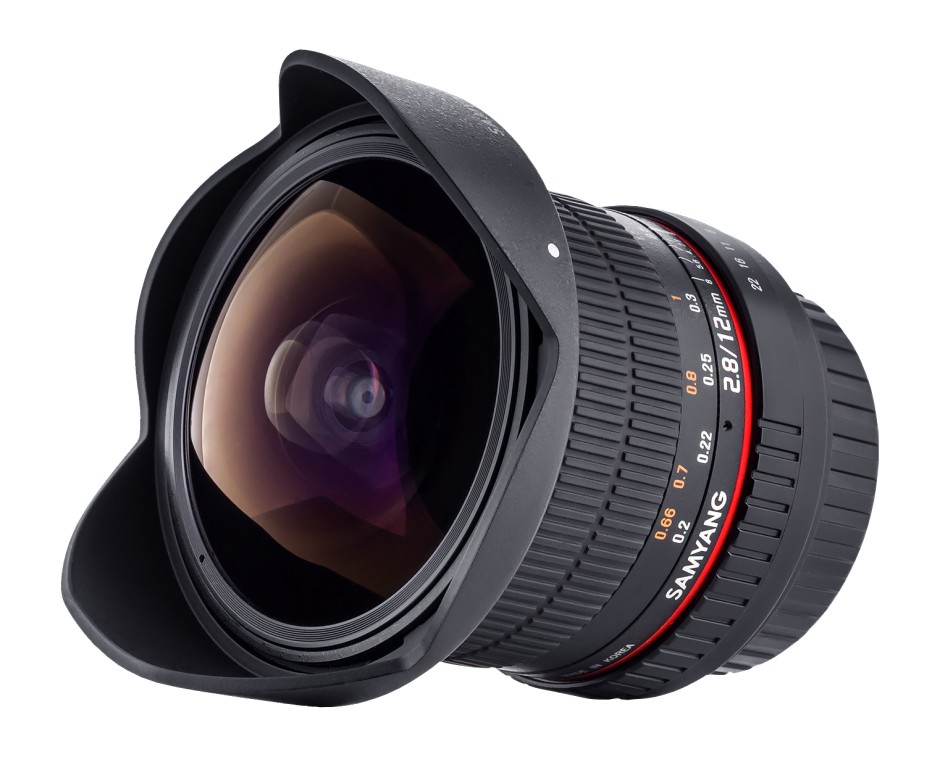
Samyang
As well as the 50 mm T1.5 AS UMC cine lens, Samyang also announced its 12 mm ƒ/2.8 ED AS NCS fish-eye lens, which has been designed for full-frame cameras. We don't have a price or release date yet for it, but I am looking forward to seeing it.
Sigma
Sigma announced its dp1 Quattro camera, with a Foveon direct image sensor that is similar to traditional colour film in that its multiple layers capture all of the information that visible light transmits. It also announced two different versions of the same lens: the 150-600mm F/5-6.3 DG OS HSM Sports and the 150-600mm F/5-6.3 DG OS HSM Contemporary. The sports version is, probably quite obviously aimed at sports and wildlife photographers. The contemporary label is more compact and portable.
There was also the 18-300mm F/3.5-6.3 DC Macro OS HSM Contemporary lens.
Sony
Just before Photokina, Sony announced two new lens units, to attach to smartphones. These were the QX1 and QX30. During Photokina, a slew of camcorders, video cameras, and accessories were unveiled, too. The things that caught my eye was the flash unit, the HVL-F32M for $300.
Sony's A5100 is available to pre-order from Adorama
Sony announced its A5100 yesterday. It has been referred to as both a replacement for the NEX-5T and as a camera sitting between the A6000 and the A5000. It has a 24.3 mepagixel CMOS sensor, auto-focus that's been described as 'lightning fast' (although not quite as fast as the A6000), upper sensitivity of ISO 25,600, a pop-up flash, wi-fi, and a touchscreen. But there's no EVF.
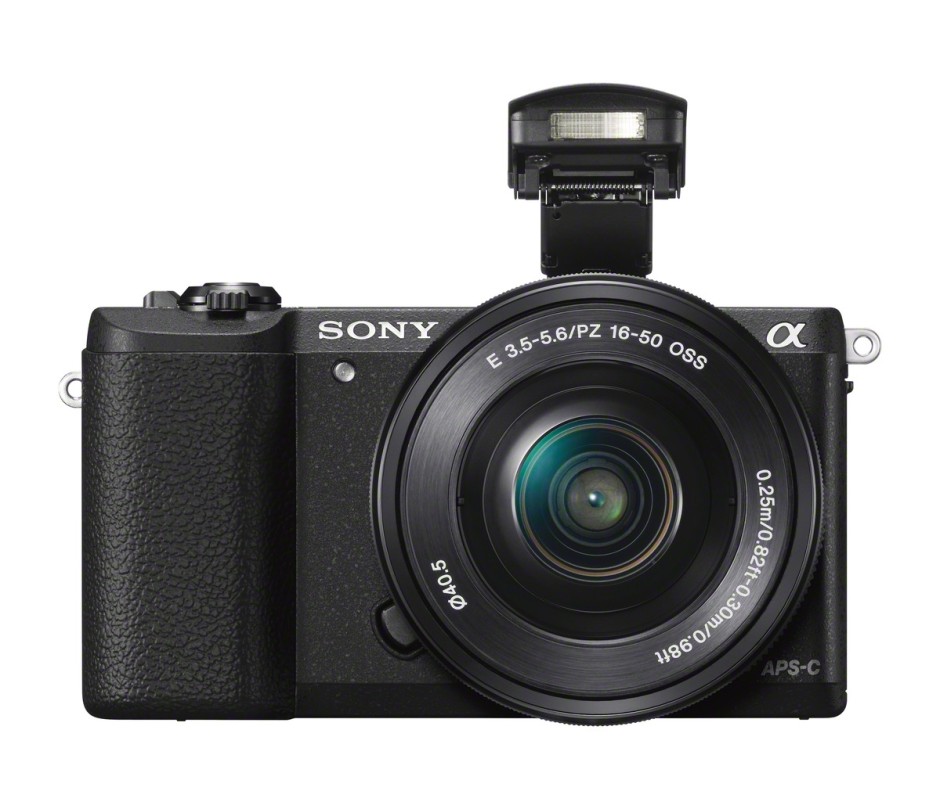

It'll come in black or white and Adorama has them available for pre-order. Body-only, it'll cost $550; if you'd prefer an A5100 with the 16-50mm lens, that'll be $700.
Making a Pringles Can Obscura
I spent Saturday at the Cambridge Festival of Science and Royal Photographic Society's photography day, listening to talks on megapixels and watching videos of caesium react with water in slow-motion. It was mostly a fun and informative experience, but apart from the caesium videos, the best bit was sitting inside Fotonow's Camper Obscura. That, just as its name suggests, is a camper van that has been transformed into a camera obscura. A camera obscura is the basis of any photographic camera, from a pinhole to a dSLR. A camera obscura is literally a dark (obscura) room (camera) with a hole poked into it, through which light can pass to create an image of the outside world on a screen. There are room-sized camerae obscurae in Bristol and Edinburgh, but they don't have to be walk-in activities. It's easy enough to scale them down and make something portable. I was aiming for something more along these lines when I decided to devise my own.
Of course, if you replace the screen with photo-sensitive paper you have a pinhole camera and by steadily improving the light-gathering and focusing abilities of the hole, with lenses, you end up with a camera more akin to those we use every day. But that's another project for another day.
Undeterred, I looked around for some DIY camera obscura instructions and found the perfect example on Exploratorium, which used a Pringles can. Seeing as Haje has already used a Pringles can to create a cheap macro extension tube, it seemed entirely appropriate to transform the snack container into a portable camera obscura. A Pringles Can Obscura.
1. Take one Pringles can
After securing a can of Pringles either from a nearby shop or your pantry, you'll need to divest it of its contents—whether you eat them all or transfer them to a new container is up to you—and then wipe it clean and keep the lid.
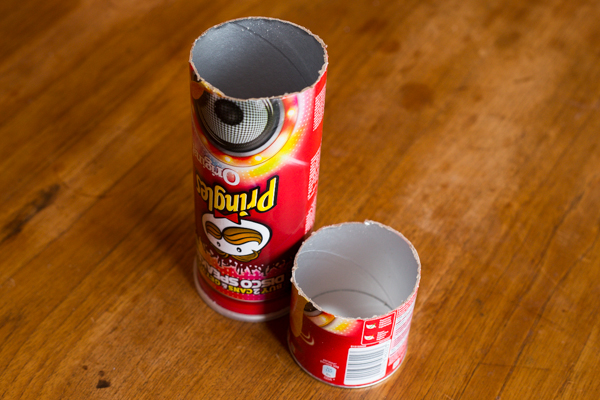

Draw a line around the tube, about 6cm or 2½" up from the base. Using a craft knife, or in my case, a bread knife, cut through the tube so that you're left with two pieces. The shorter section will be from the bottom of the can, and the longer section from the top.
2. Make a screen
You need to make a screen onto which your image will be projected inside the can. The cheapest and most readily available means to make one is from tracing paper.
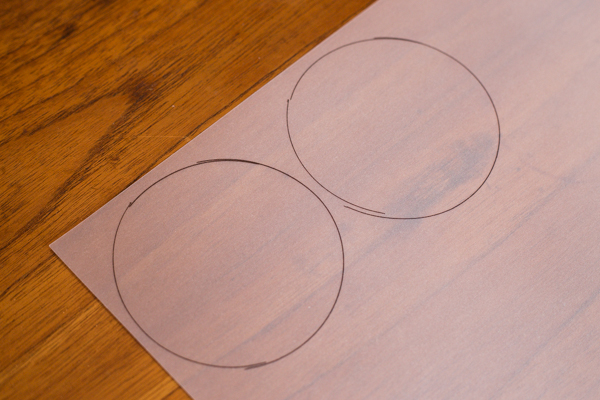

Place the lid of the Pringles can on a sheet of tracing paper, draw around it, and then cut it out. Secure the tracing paper on to the top of the tube using the lid.
3. Put the can back together
Rather than reconstruct the can with the two cut ends meeting again, you want the cut end from the bottom section of the can meeting the lidded, tracing-papered end from the upper section. Secure them in place using gaffer tape or electrical tape. No light should be able to pass through the join.
I got so carried away sticking it together that I forgot to take a photo. I'm sorry.
4. Pierce a hole
In order for the light to pass into the can and create an image, pierce a hole using a drawing pin in the base of the can.
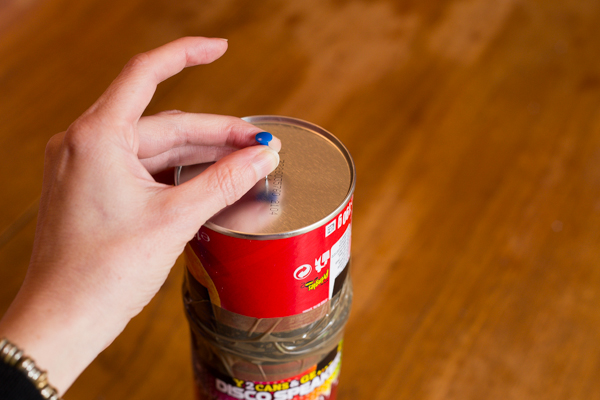

5. Finish off your Pringles Can Obscura
To make sure that you don't end up with spurs of cardboard poking into your face when you hold your Pringles Can Obscura to your eye, tape up the cut surface with some electrical tape. And if you don't want it to resemble a Pringles can that you've hacked up, wrap some coloured paper around it.
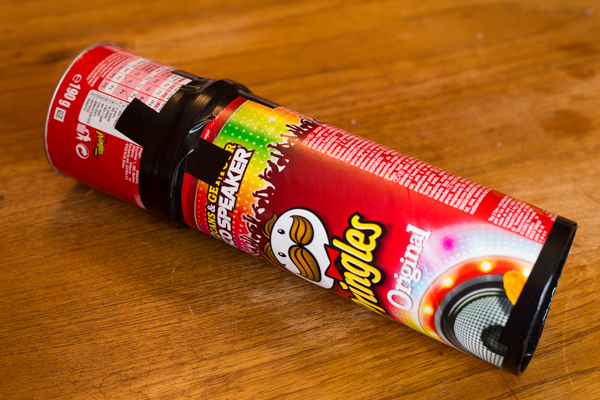

6. Head out into the light
The brighter the day, the better the image you'll be able to render on your screen. Just remember that everything will appear upside down. And then it will be a case of moving nearer and farther away from your subject to get it in focus.
It's a great tool to remind you just how simple the principles of photography are, and to get you back in touch with moving subjects into and out of focus.
(And don't go getting any ideas about the gorgeous image of the tree. That's obviously, from the Camper Obscura.)
An order of smartphone camera units suggests Amazon might be venturing into phones
Rumours of an Amazon mobile phone aren't exactly new. Speculation started when the Kindle was released; it heightened when the Kindle Fire came out; it has rumbled on since then with suggestions first that Foxconn might be manufacturing the handsets, and then HTC. Now it's being reported that Amazon has placed orders for smartphone compatible compact camera modules with Taiwanese manufacturer Primax Electronics, ready to launch a new device in the first half of 2014. I've not been able to dig up any more information on the camera unit specs, but even with a world-beating camera, any Amazon smartphone is going need to strong hold in the app market. Apart from an interface that not everyone gets along with, the Kindle Fire's primary shortfall is its lack of apps. If Amazon wants to compete in the mobile market, whatever the price of the device, this is something that will need to be addressed.
(Headsup to TechRadar)
Triggertrap Redsnap goes live on Kickstarter
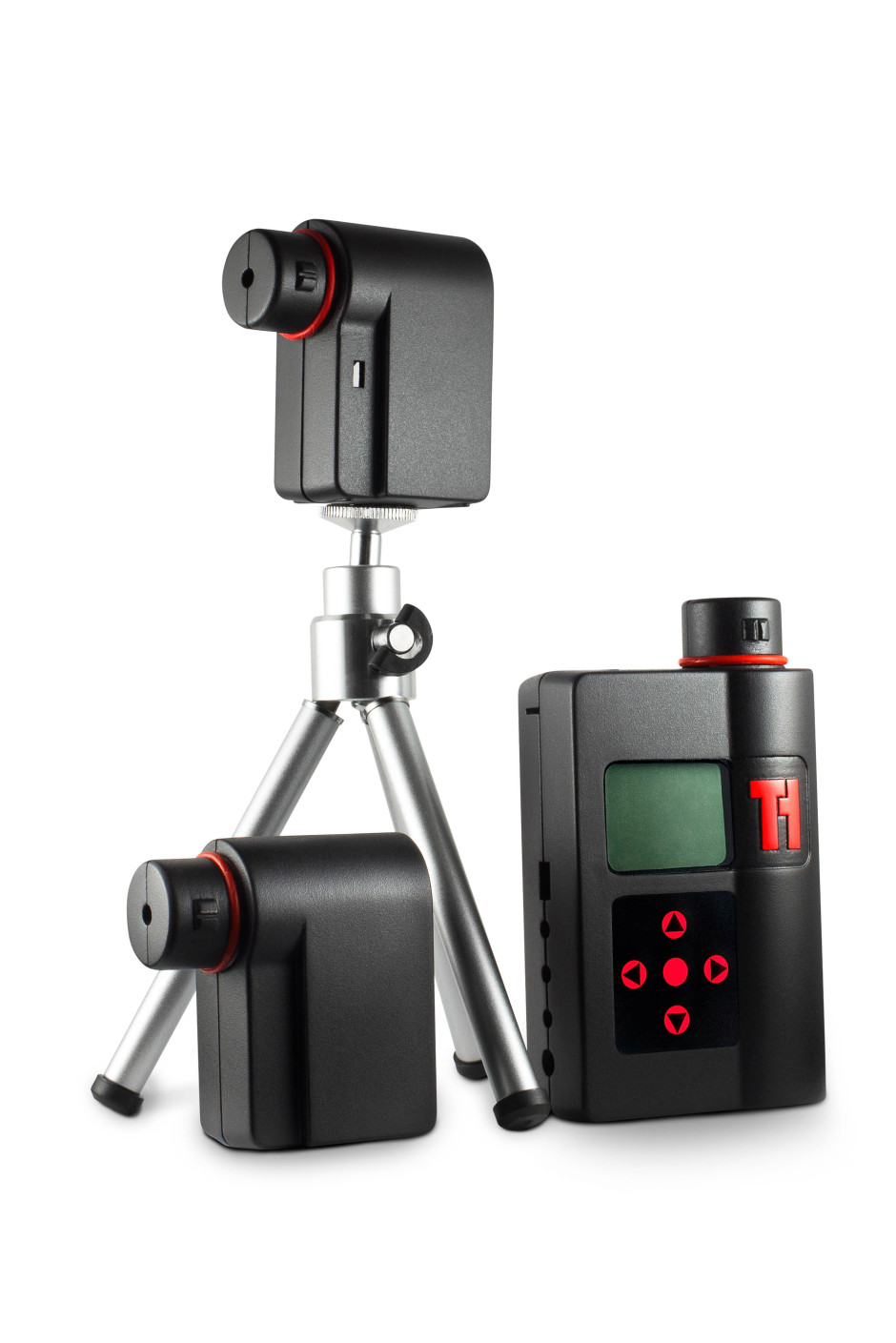
When Haje Jan Kamps (that is the very same Haje Jan Kamps who publishes Photocritic) launched his first Kickstarter project to deliver the Triggertrap universal camera trigger, back in 2011, little did he know that it would spawn a mobile app with 14 ways to trigger your camera, a high-speed triggering device, and an actual company with offices and employees. Now, Triggertrap is returning to Kickstarter to bring you Redsnap: an infinitely expandable high-speed camera triggering tool. Redsnap is a modular system, offering photographers the ability to build the camera trigger that they need for each shoot.
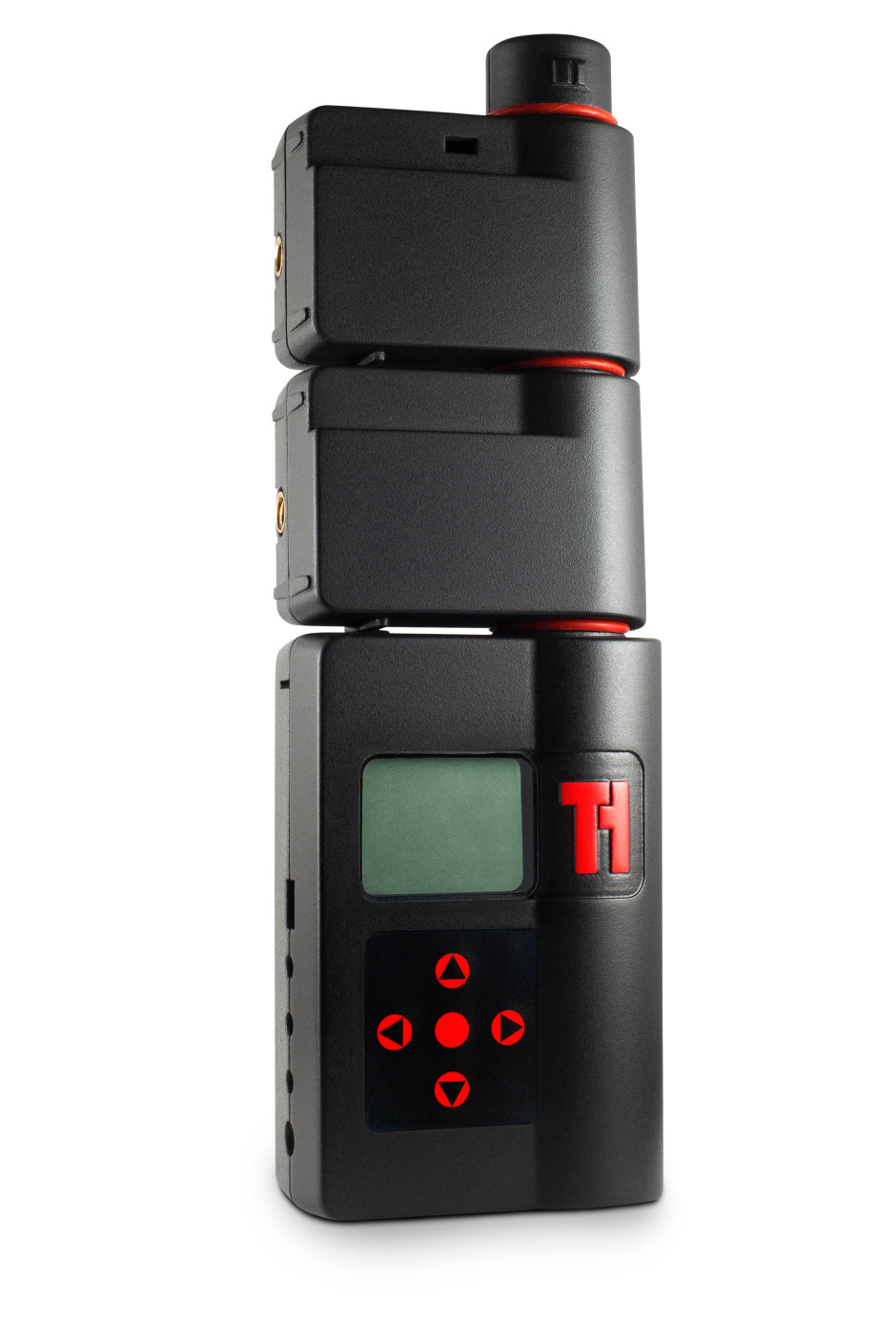

The base block includes the time-lapse options Triggertrap is known for: timelapse, TimeWarp (timelapses that include acceleration), long exposure HDR, and star trail mode. On top of that you can add a high speed laser sensor, great for capturing a bullet in flight; a high speed sound sensor, to capture bursting balloons and smashing vases; a high-speed light sensor to make sure you snap a lightning strike; and a passive infrared sensor (PIR) that's ideal for stalking lions and tigers and bears. Or butterflies, if you feel like something a little less adventurous. That's the initial offering of modules; more are in the works.
Redsnap has three outputs to connect it to three cameras, three flashes, or a combination of both. There's also a connector that allows it to communicate with the Triggertrap mobile device, bringing its triggering options into play, too.
What do you get for your Kickstarter backing, then? The timelapse kit is £35; the wildlife kit is £120; and multiple-sensor kits are priced between £125 and £190. If you're really, really desperate, you can pledge £1,000 and be first in line for a pre-production prototype.
Even more information awaits you on the Kickstarter page, and of course there's a video, too.

Learning by doing with the Bigshot DIY camera
I've just stumbled across a magical photographic triumvirate: DIY, getting kids involved in photography, and education. It's called the Bigshot Camera: a self-assembly camera that teaches whomsoever is building it, whether aged eight or 108, about key science concepts in the process. It's a rather tasty science and creativity sandwich.
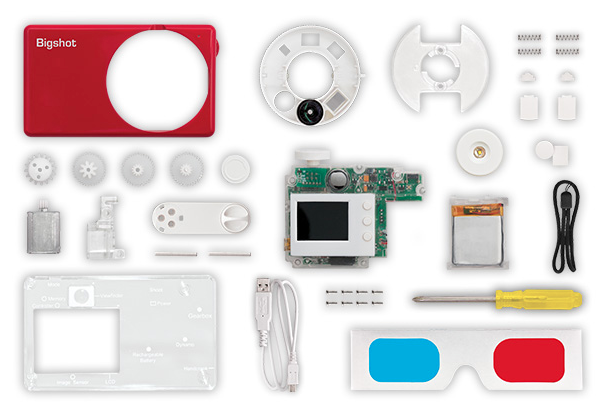
The camera has to be assembled in a specific order, but there are detailed instructions on the website to make sure that you get it right. Even more importantly, as you work through each stage you have the opportunity to learn about the science underpinning it, from optics to mechanics via electromagnetism and electronics, and back again. When it's complete, you should have a fully functional camera with a rotating wheel that houses normal, wide-angle, and 3D-capable lenses. If the battery dies, you can crank it back into life yourself.
One of the motivating factors behind Bigshot is learning by doing, and inspiring young people to get involved with science and engineering. It's the sort of project that a parent (or auntie) can work on with their child (or niece... I'm looking at you, Eva), but there's plenty of support for teachers who want to incorporate it into their teaching plans, too. Each camera costs about $90, but Bigshot has an extensive outreach programme, Bigshot for Good, that aims to bring the project to less privileged children, wherever they are.

From an idea that sprang to life in 2006, the Bigshot has been developed by Shree Nayar, a Professor of Computer Science at Columbia University. Along the way he has received research and design support from students led by Guru Krishnan and Brian Smith and funding support from a Google research award and an ONR Instrumentation Grant. Nayar founded Kimera, a social venture aimed at bringing the Bigshot to children and teachers the world over, in 2011. And from this month you can go ahead and order yourself one from the Bigshot website.
As for future plans, the Bigshot team is exploring two potential avenues: to continue to deepen the Bigshot camera experience by developing new features and enhancing the learning platform, or to develop other gadgets that lend themselves to the Bigshot concept of building, learning, and using.
The Bigshot website is well worth a wander: it's a veritable hive of knowledge and information, whether or not you want to buy a camera. Me? I'm totally in the queue for when they start shipping beyond North America!
Review: Think Tank's Streetwalker Pro camera bag
When Think Tank offered me the chance to spend some time schlepping around my gear in one of their bags to see how it (and I) fared, of course I said yes. Legions rave about their bags and I wanted to give one a go for myself. So I opted for a Streetwalker Pro (the name does have dodgy connotations, I know) and it and my photographic impedimenta have been inseperable since its arrival.
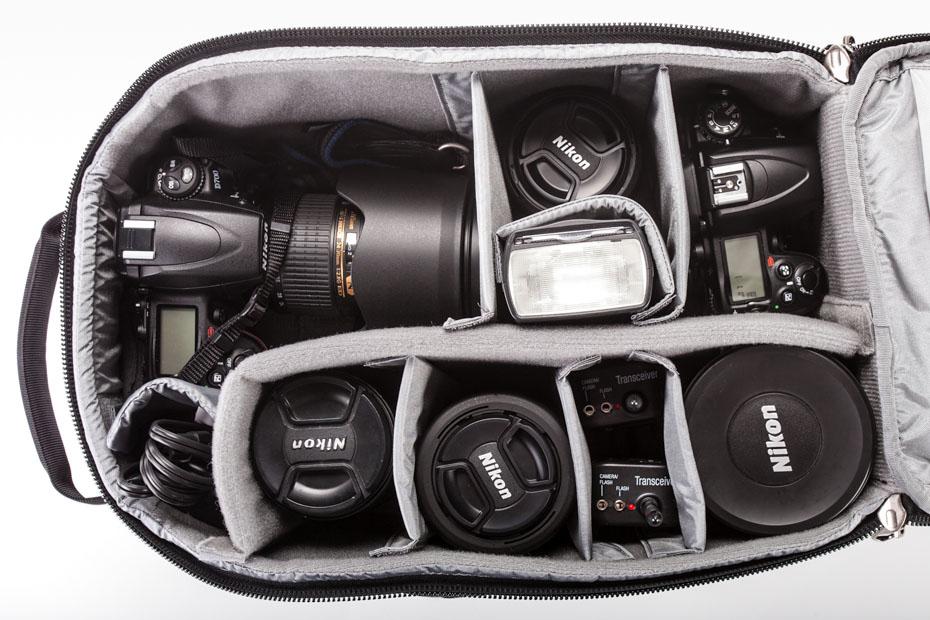

The Streetwalker Pro is intended for use on the move—days out and expeditions when you'll want a goodly selection of gear—but not necessarily travel. There's no laptop compartment in the Streetwalker Pro; for one of those, you'll need to look to its slightly larger companion, the Streetwalker Pro Harddrive. When I say I goodly selection of gear, I really mean it. This bag is a veritable TARDIS. It comfortably holds a full-frame body, a 70-200mm, and between two and four other lenses. You can play divider Tetris and get flashes, cables, remote releases, and all sorts in there, too. It has more pockets than I know what to do with. There's a tripod carrying-system. And it comes with a waterproof cover. If I were to fill it completely, I'd probably not be able to pick it up.
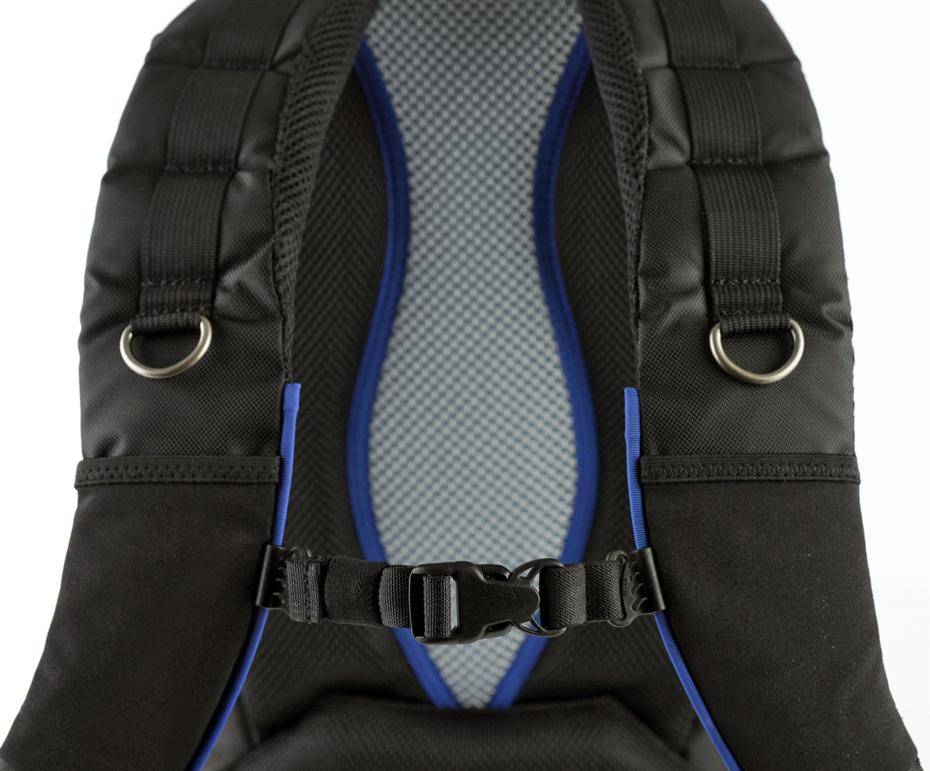

It's also a taller, narrower bag than your average camera bag. For little me, this is a huge boon. I often find myself waddling about beset by a bag that makes me twice as broad as I am normally, which screws with my spatial awareness, particularly when in crowded places. It's plenty comfortable with well-padded straps. The internal padding leaves your gear feeling secure and the build quality means that you don't fear the bag faling apart on you.
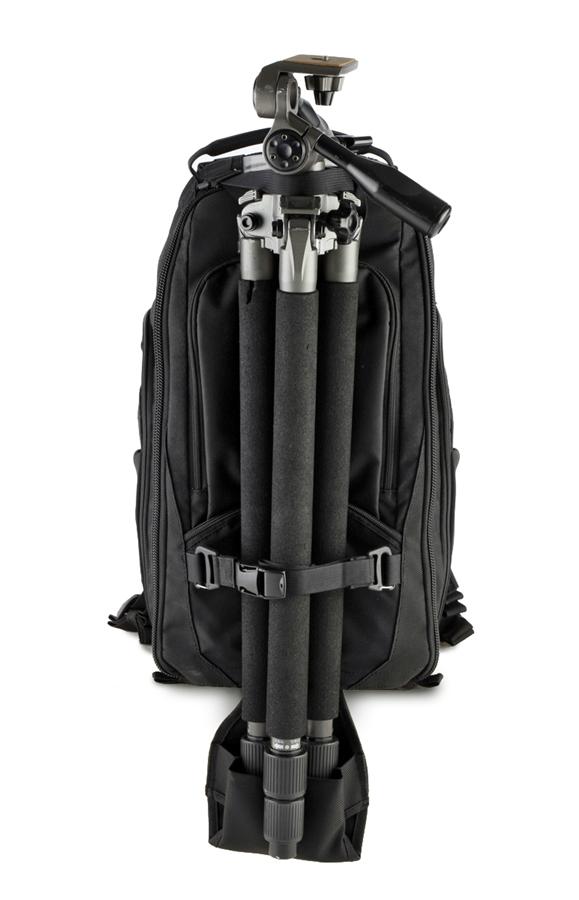

As it's a day-out-taking-photos-bag, having somewhere to put a sweater would be useful, but there's that much space in the bag you could probably stuff it in and not worry too much. If some of the pockets expanded a little more, that would be useful. My biggest concern, however, was that I found I needed to set it down every time that I wanted to open it up, particularly if what I wanted was towards the bottom of the bag. Other people might not find this so problematic, but I'd appreciate some easy-access zips.
At $190, the Streetwalker Pro is a good bag, but it isn't perfect. My quest for the perfect camera bag continues!















